Cats v Dogs
A Data Streaming application that analyses Tweets in real-time to determine whether cats or dogs are more popular on Twitter at any given time.
Objectives
The goal of this project was to learn the fundamental components of a data streaming pipeline by finding a simple, highly abstracted cloud-based method to analyse & visualise a data stream in real-time.
The application aims to analyse the popularity of cats and dogs on Twitter at any particular point in time and visualise its evolution in real-time on a dashboard. Popularity is judged simply by the number of tweets coming through with cat or dog related hashtags. This first implementation was kept as simple as possible as a proof-of-concept of the end-to-end pipeline and further complexity will be added to the application gradually.
The corresponding code is available on my Github page here
Architecture
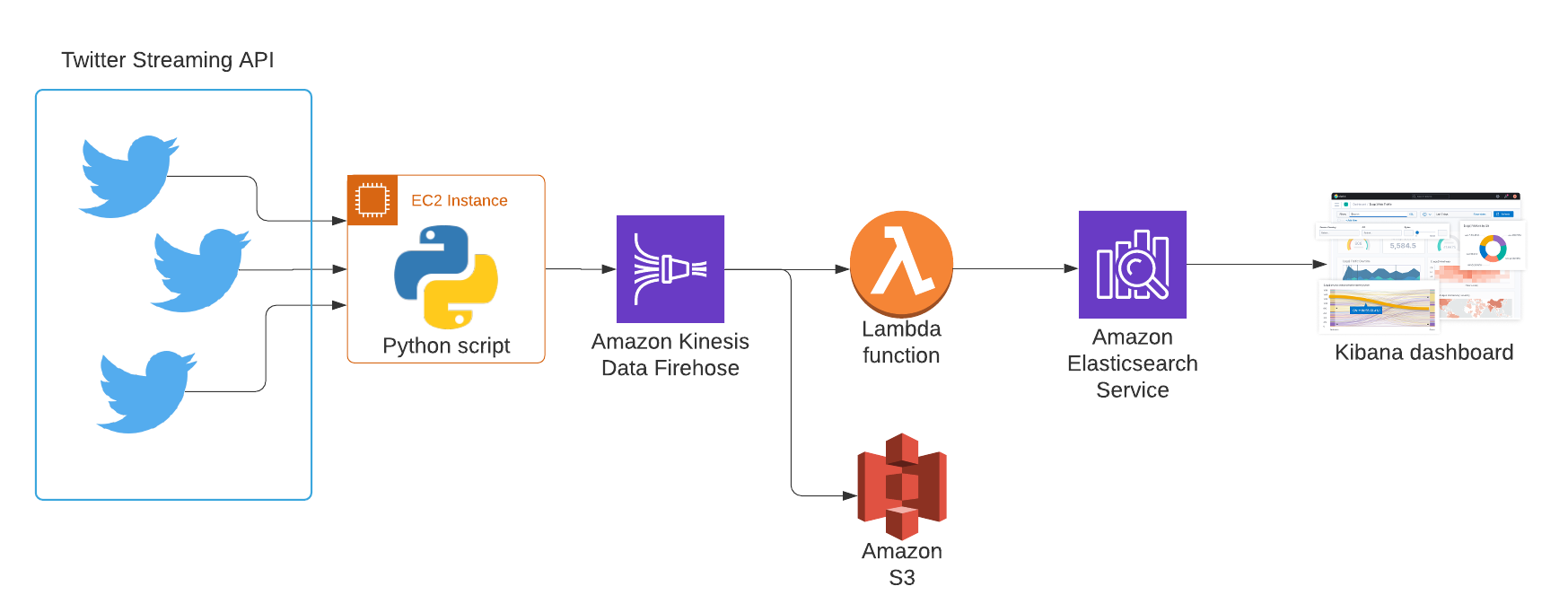
Twitter API and Python Script
The Python script serves two main purposes:
- It connects to the Twitter API to set the rules that specify which Tweets will be streamed. The stream will only include Tweets with hashtags related to cats or dogs that also contain images or videos.
- It then opens a persistent connection to the Twitter Filtered Stream API and ingests the streaming Tweet objects into the Firehose Delivery Stream. The fields contained in the Tweet objects are determined by the HTTP query parameter. In this particualr implementation, the following fields are included: Tweet Id, Retweet count, Reply count, Like count, Quote count, Tweet text (including hashtags), Matching rules id, Matching rules tag.
The script contains a loop to automatically reconnect if the stream is disconnected or encounters any exception such as unexpected record formats.
AWS Firehose Delivery Stream + Lambda function
The Kinesis Data Firehose service ingests, transforms and delivers the streaming data records to Elasticsearch. It also delivers a back-up of each record to an S3 bucket.
The Lambda function processes each record as it goes through the stream. It cleans up each Tweet, keeping only the relevant fields for further analysis (the granularity of the Twitter query parameters allowed means that some fields are included by the Twitter API by default and need to be pruned to save on space and compute time). It also adds a timestamp and converts the record to JSON format (required for Elasticsearch) before pushing the record back into the Firehose stream for delivery to its destination.
Elasticsearch + Kibana
Elasticsearch is a distributed, JSON-based search and analytics engine. The AWS ES service is a fully managed service to deploy and run an Elasticsearch cluster. The integration with Firehose in AWS is pretty seamless and the schema of the records is automatically recognised by ES and reflected into an ES index.
The real-time visualisation dashboard was created using Kibana, which comes built-in with Elasticsearch. It displays a number of metrics and updates automatically every 60 seconds.
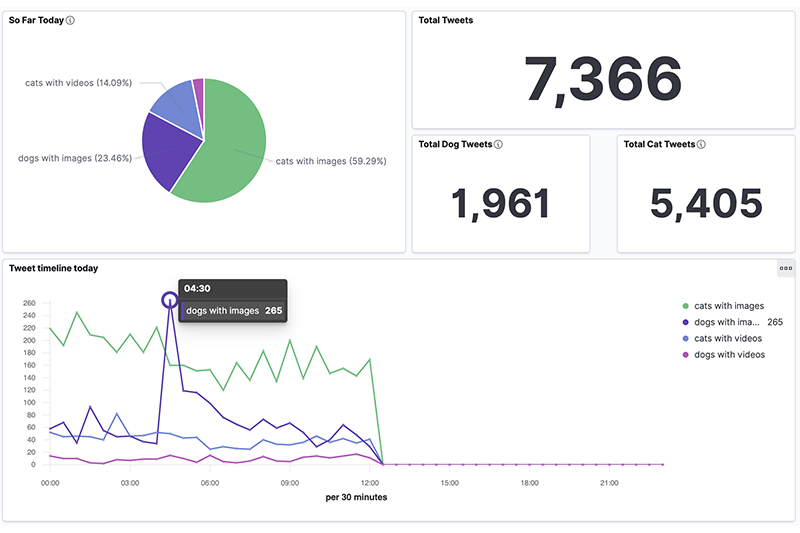
Plans & ideas for enhancements
- Additional in-stream analytics with a more accurate method to assess popularity. For example, using the number of likes or retweets as they add up throughout the day. All tweets come in only once, with 0 likes in the count field. This would require a separate piece of functionality with continuous API calls to retrieve the latest like count for each tweet previously streamed by the application.
- Exploring the full capabilities of Elasticsearch & Kibana for more sophisticated analytics and visualisations (e.g. highlighting the most popular Tweet of the hour, text field reacting to the data evolution in real-time etc...)
- Including a call to an ML model to determine the sentiment of each streamed Tweet. A Tweet with a negative connotation should be be excluded from the count that determines popularity